Oct 6, 2011 - Download. Thank you shekhar for the ppt. Consumer Behavior Chapter 4 Version 3e Processes a consumer. Buying Behaviour Model The Economic Model: A man divide his fixed income in a certain rational way. Jan 14, 2018 - Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior Cultural factors Social factors Personal factors Psychological factors. Consumer Behaviour Models Ppt.
Consumer Behaviour Models Chapter 3 Consumer Behaviour Models Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Chapter Objectives To understand the role consumer behaviour plays in the development and implementation of advertising and promotion programs. To understand the consumer decision-making process and how it varies for different types of purchase.
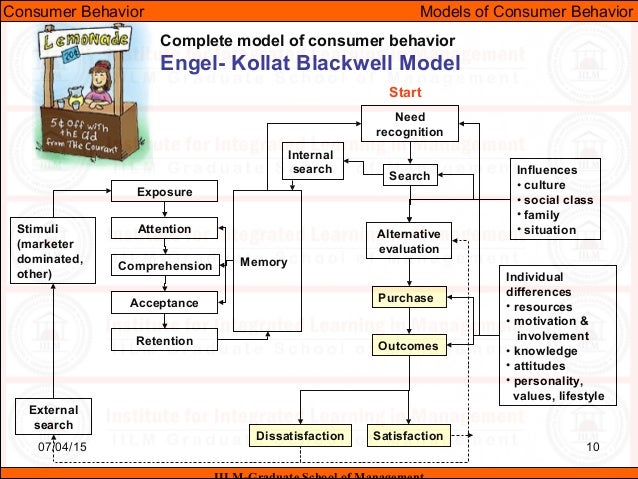
Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Chapter Objectives To understand various internal psychological processes, their influence on consumer decision making, and implication for advertising and promotion. To recognize external factors such as culture, social class, group influences, and situational determinants and how they affect consumer behaviour. Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Consumer Decision Making Process Need Recognition Information Search Alternative Evaluation Purchase Decision Postpurchase Evaluation Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Consumer Decision Process Need Recognition Information Search Alternative Evaluation Purchase Decision Postpurchase Evaluation Motivation Perception Attitude Formation Integration Learning Decision Process Stages Psychological Processes Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Sources of Need Recognition Out of stock. Purchase decision is routine. Resolved by choosing familiar brand.
Dissatisfied with current state of product/service. Advertising is used to help consumers recognize need for new product. Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Sources of Need Recognition New needs or wants. Created by life changes. Graduation, employment status, financial situation).
Wants are desired but not essential. Related product purchase. Purchase of a new product will most likely trigger purchase of accessories. New camera will require film). Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Sources of Need Recognition Marketer-induced recognition. Marketers’ encourage discontentment with current state or situation.

Brand switching is encouraged by sales promotion. New products. Innovative products may stimulate a need. Consumers may not see a need for what the marketer is selling.
Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Examining Consumer Motivations Marketers recognize need recognition will influence the remainder of the decision process. To better understand consumer’s reasoning marketer’s devote considerable attention to motives. Motives - factors that compel a consumer to take a particular action. Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Self-actualization needs (self-development, realization) Esteem needs (self-esteem, recognition, status) Social needs (sense of belonging, love) Safety needs (security, protection) Physiological needs (hunger, thirst) Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Market Research Methods In-depth interviews. The consumer talks freely in an unstructured interview to obtain insights into his or her motives, ideas or opinions.
Projective techniques. Methods allowing consumers to project values, motives, attitudes or needs on some external object. Chapter 3: Consumer Behaviour Models Market Research Methods Association tests.
Consumers respond with the first thing that comes to mind when presented with some verbal or pictorial stimulus. Focus groups. A group of consumers with similar backgrounds or interests discuss a product, idea or issue.
.how the product will be adopted by the consumers. Consumers always demand value for their money when they making any purchase. Companies always seek to understand consumer behavior with respect to product development (Blackwell et al, 2005). Waptrick black berry 9250 free games. Customer preferences change with time and, therefore, continuous assessment of the market is needed.
The aim of research is to make sure customers derive satisfaction after consuming the goods, hence, buy more. Buyers’ behaviour is determined by various factors such as attitudes, personality, motivation, gender and the environment in general among others (Folkes, 2006). On the other hand, Blackwell et al (2005) argue. .-1883 PR Newswire, 2010, 'Coffee Consumption Continues to Grow Amongst Brits - Rogers Estate Coffees Offers 12 Bags for the Price of 8 on Wholesale Coffee Purchases to Help Retailers Meet the Demand', New York: Apr 15, 2010 Ratneshwar, S Shocker, AD Cotte, J & Srivastava, RK 1999, ‘Product, person, and purpose: putting the consumer back into theories of dynamic market behaviour’, JOURNAL OF STRATEGIC MARKETING.